1. Introduction
Background
Asian disaster statistics indicate that the Asia-Pacific region suffers disproportionately from natural disasters. Over the last 30 years, the region has been impacted by some 37% of disasters recorded worldwide, and accounts for 57% of global fatalities and 89% of the total victims associated with such disasters.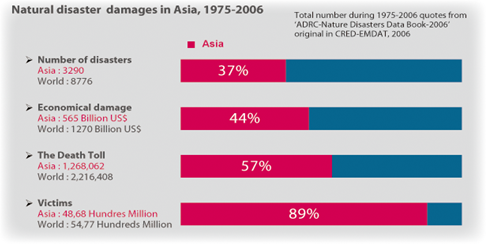
Considering these distressing statistics, the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF) in 2005 proposed an initiative called Sentinel Asia, to showcase the value and impact of Earth observation technologies, combined with near-real-time internet dissemination methods and Web-GIS mapping tools for disaster management support in the Asia-Pacific region.
Many of these goals are possible only through the wide-area and fast response collection of images and other data which can be acquired by Earth observing satellites. Sentinel Asia is a voluntary and best-efforts-basis initiative led by the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF) to share disaster information in near-real-time across the Asia-Pacific region, using primarily the Web-GIS technology. Its architecture is designed to operate initially as an internet-based, node-distributed information distribution backbone, eventually distributing relevant satellite and in situ spatial information on multiple hazards in the Asia-Pacific region.
History
”Sentinel Asia” was originally proposed in November 2004 when it was realized that maximum benefit from rapid technological advances in the region would occur, and this data could be delivered more quickly via the internet as easy-to-interpret disaster-related information. SA is not designed to replace already active efforts by many of our regional agencies in delivery of information to emergency services. Rather, it aims to expand such efforts and make such data available to all countries and many more people in the region, particularly in countries that do now their own satellite reception facilities. Through such a backbone, information about disasters could begin to be delivered more efficiently through the ’world-wide-web’, even outside national borders, in ’real-time’ or ’near real-time’, and used as early-warning, or as post-disaster information by various countries and relevant end-user agencies.
So, the decision was made soon after the Indian Ocean tsunami disaster to fast-track this project and compliment current space, and ground infrastructure in the region with a fast distribution system of disaster-related earth observation information to relevant agencies and the public throughout the region. The technical concept for Sentinel Asia was finalized at a meeting in May 2005 in Kuala Lumpur, hosted by the Malaysian Center for Remote Sensing - MACRES, and promptly approved as a project for rapid implementation by the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum-12 (APRSAF-12) Plenary held in Kitakyushu, Japan, in October of 2005. In APRSAF-12, the ”Disaster Management Support System in the Asia-Pacific Region (DMSS)” proposed by JAXA is designed to showcase:
- Construction of a ’life-first society’ by ICT & Space technology
- Improvement of speed and accuracy for disaster preparedness and early warning
- Minimizing victims and social economic losses due to disasters
A stepwise approach for implementation of this dissemination system was proposed by the APRSAF Earth Observation Working Group, where:
- STEP 1: Implementation of the backbone ’Sentinel Asia’ data dissemination system and associated Nodes, to showcase the value and impact of the technology using standard internet dissemination systems (February 2006 - December 2007)
- STEP 2: Expansion of the dissemination backbone with new Satellite Communication Systems (2008 - 2012)
- STEP 3: Establishment of a comprehensive DMSS (2013 and onwards)
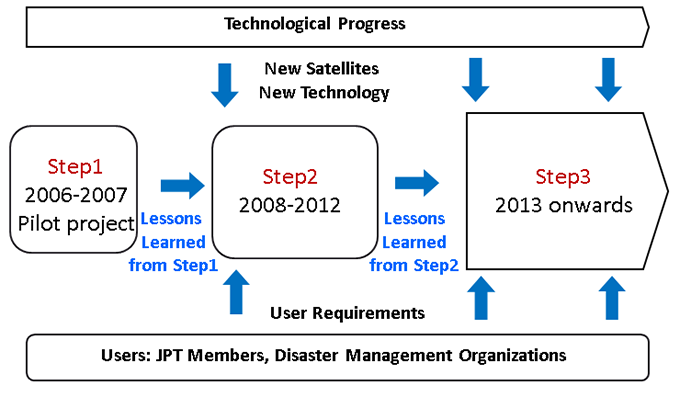
This document covers primarily STEP 2, the Sentinel Asia backbone system which utilizes the communication satellite, WINDS (Internet and Wideband InterNetworking engineering test and Demonstration Satellite) was opened on October 2009. This initiative is to be closely coordinated with similar initiatives elsewhere in the world (e.g. NOAA-EUMETSAT and GEO-Netcast). The DMSS is a component of a wider initiative outlined at a specialized workshop for the United Nations World Conference on Disaster Reduction in Kobe - Japan, 20 January 2005.
2. Basic Concept of STEP 3
The Sentinel Asia is a voluntary basis initiative led by the Asia-Pacific Regional Space Agency Forum (APRSAF) to support disaster management activity in the Asia-Pacific region by applying the WEB-GIS technology and space based technology, such as earth observation satellites data.
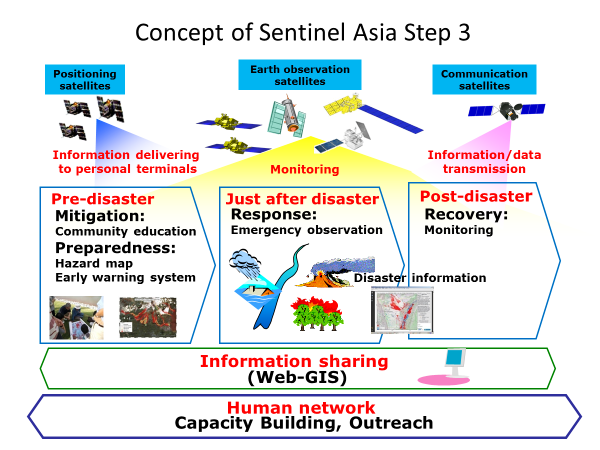
A step-by-step approach was adopted for the implementation of Sentinel Asia. In the current step, the STEP 3, it is expected to implement not only emergency observation but activities covering entire disaster management cycle including mitigation/preparedness and recovery phase after a disaster so that the space-based technology would contribute to more activities for mitigation/prevention of natural disasters in Asia and the Pacific.
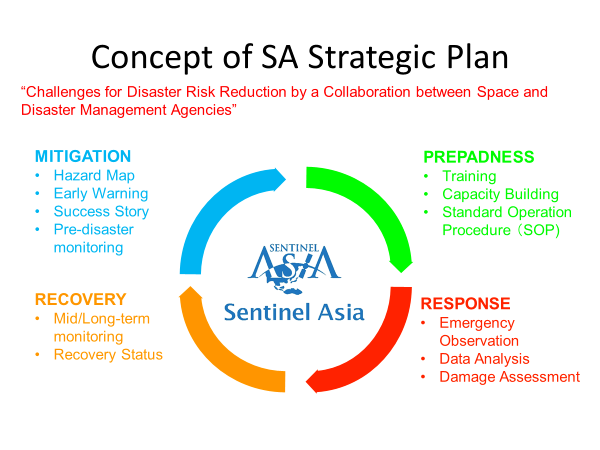
To achieve these goals of STEP 3, Steering Committee will review previous activities, identify problems, propose solutions and lead to implement those suggested ideas and proposals to enhance the contribution of space based technology to DRR (Disaster Risk Reduction) by closely working with technical agencies as well as end user agencies related to DRR.
3. Main Activities
1. Emergency observation by earth observation satellites in case of major disasters
Current registered satellites are ALOS-2 (JAXA), Resourcesat-2, CARTOSAT-2, RISAT-1 (ISRO), Thaichote (GISTDA), VNREDSat-1 (VAST), TeLEOS-1 (CRISP), DubaiSat-2, KhalifaSat (MBRSC) and FORMOSAT-5 (TASA).2. Acceptance of observation requests
JPT members or ADRC member organizations are entitled to make emergency observation requests (EORs) to Sentinel Asia. When EORs are accepted, subject to their availability, the following satellite data will be acquired and provided: ALOS-2 (JAXA), Resourcesat-2, CARTOSAT-2, RISAT-1 (ISRO), Thaichote (GISTDA), VNREDSat-1 (VAST), TeLEOS-1 (CRISP), DubaiSat-2, KhalifaSat (MBRSC) and FORMOSAT-5 (TASA).3. Wildfire Working Group, Water related disaster Working Group and Tsunami Working Group
To accelerate the utilization of satellite-derived products related to disasters by end-users, working groups have been set up within the framework of Sentinel Asia to focus on specific disasters and to include specialists and researchers in each specific field.
4. Fast Sharing Data
The vision for Sentinel Asia is that it will be a fundamental service distributing, (in near real-time where possible,) only disaster-related data products/images in the Asia-Pacific region as follows:
- Satellite imagery (and data permitted by data provider) provided by space organizations
- Value-added images with extraction of stricken area, etc. created from satellite data
- On-site digital camera images
- Wildfire hotspot and rainfall information derived from satellite data
- Meteorological satellite information
- Basic map data is OpenStreetMap and so on.
- Fine regional digital maps contributed to the network by national geography organizations, etc.
In addition, through the close links to Asian Disaster Reduction Center (ADRC) additional information will be available such as:
- Detailed disaster information
- Regional social / economic data
Main products provided by Sentinel Asia are as follows:
- Satellite imagery (and data permitted by data provider) and value-added images with extraction of stricken area, etc.
- On-site digital camera images
- Wildfire hotspot information and data
- Rainfall (short-term and long-term) information and data
- Meteorological satellite imagery and data
5. Framework
Sentinel Asia is promoted under cooperation among the following three communities: Space Community (APRSAF); International Community (UNESCAP, UNOOSA, ASEAN, AIT etc.); Disaster Reduction Community (ADRC and its member countries).
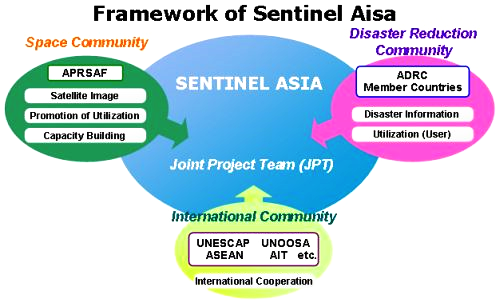
< Joint Project Team (JPT) >
To promote Sentinel Asia, the Joint Project Team (JPT) was organized. JPT is open to all the APRSAF member countries, disaster prevention organizations and regional/international organizations who wish to participate in disaster information sharing activities.
< Nodes and Working Groups >
Operationally Sentinel Asia is composed of two Nodes and three Working Groups.
Data Provider Node:
Data Provider Node provides their own satellite imagery and/or data to JPT members upon the emergency observation request from JPT member to the extent permitted by the data policy of each DPN when disaster happens.
Data Analysis Node:
Data Analysis Node analyzes the satellite data provided by DPN, makes value added product and discloses the result through the Sentinel Asia System within the domestic legislation of each DAN permits.
Wildfire Working Group:
Wildfire Working Group works for the establishment and improvement of early forest fire detection based on CIRC data, development of forest fire expansion forecasting and serving value-added information to forest fire control agencies.
Water related disaster Working Group:
Water related disaster Working Group works for exchanging ideas with regards to water related disasters reduction by using aerospace technology together with ground survey and GIS/Mapping technology especially in the field of flood, land slide, flash flood, drought, storm surge and so on caused by heavy rain, typhoon, tropical cyclone, monsoon and climate change.
Tsunami Working Group:
Tsunami Working Group works to contribute for enhancing capabilities of Tsunami disaster management in Asia-Pacific countries. (1) Tsunami Risk Assessment (2) Tsunami Forecasting/Warning (3) Mapping Tsunami Inundation/Impact (4) Tsunami Evacuation Plan (5) Emergency Observation (6) Tsunami Risk Awareness/Education (6) Training Program/capacity building.